How GenAI is Transforming What’s Possible in CRE
EY's Umar Riaz on the why and how of implementing a GenAI strategy.
Generative AI is the next step in the evolution of artificial intelligence. GenAI can create new content based on data it has been trained on, which will catalyze foundational shifts in business and operating models and give users the capability to perform an array of tasks at lightning speed. GenAI applications, such as ChatGPT, have already attracted a record number of users and investment from both established technology players and a wide range of startups. The potential use cases for GenAI span a wide range of functional areas, including sales and marketing, finance, operations, HR and IT. GenAI is being compared with the digital transformation that started in the early 2000s, which unleashed innovation and disruption across every industry, including real estate.
As with all new technologies, GenAI presents risks alongside the promised benefits. One of the biggest risks is the potential impact on the existing workforce with functions such as administrative support, legal, IT and customer support. As was the case with digital transformation, any negative impact on jobs will likely be balanced with the creation of a new ecosystem of jobs and functions that do not exist today. The World Economic Forum predicts automation will actually result in a net increase of 58 million jobs, replacing repetitive tasks and dangerous jobs with challenging work that creates more interfaces with customers and a better product. A lack of transparency, questions about accuracy, and the potential for bias and misinformation are some of the risks that will also need to be addressed. In addition, companies need to work through GenAI’s impact on cybersecurity, intellectual property and fraud challenges that will come into play.
Real estate is one of many sectors that could transform itself with GenAI. Real estate companies have faced an operating environment where it is challenging to attract and retain talent, meet increasing investor demands and keep up with technology trends, such as advanced data and analytics and smart buildings. In addition, real estate companies do not want to have to scale their costs in line with growth of assets under management. GenAI has the potential to help address all these challenges.
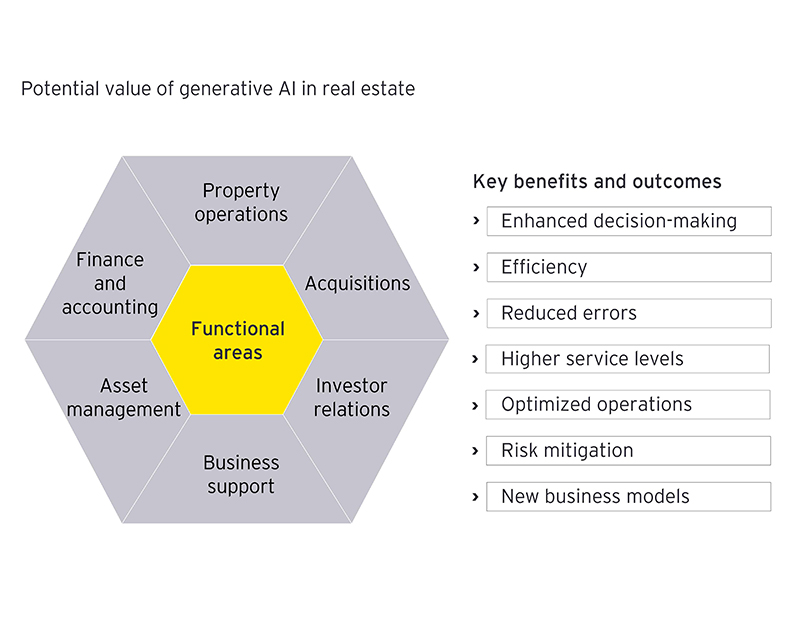
GenAI in real estate
GenAI has a role to play in creating opportunities for greater efficiency, mitigating risk through its ability to rapidly scan data and identify any concerns that may exist, and potentially paving the way for new business models. There are a number of potential use cases for AI in the commercial real estate sector across the real estate value chain:
Acquisitions: When potential acquisitions are considered, GenAI can enable automation and intelligent analytics for finding, buying and operating assets. The due diligence effort becomes less onerous and more reliable, providing important insights that either support making the move or reveal concerns that prevent a transaction that shouldn’t be made. GenAI can also enhance portfolio planning, scenario planning, contracting and financial analysis.
Investor relations: GenAI has the potential to transform customer relationship management, including investor relations. The technology can be used to better target potential investors and to maintain ongoing relationships. Generating marketing materials, investor presentations and answers to investor queries can all be streamlined using GenAI. Investor chatbots can be deployed, giving investors the ability to have their questions answered more efficiently.
Business support: HR, IT and legal are typical support functions within real estate, and GenAI has the potential to significantly impact all these areas. GenAI can be used in the hiring process by creating job specifications, screening resumes, performing background checks and supporting the interview process. Employee chatbots can streamline HR processes. AI can be used to develop and deploy code for new capabilities and to manage cybersecurity. Typical legal functions, such as contracting and document discovery, can be transformed. Procurement processes, such as vendor selection, bid analysis, purchase order generation and invoicing, can be enhanced.
Asset management: GenAI can give asset managers the tools necessary to collect and analyze property-level data more effectively. This will lead to enhanced budgeting and forecasting. There is also the potential for GenAI to be used in leasing, ESG reporting, capital planning and risk identification. Reporting and scenario planning can be streamlined.
Finance and accounting: Generations of financial reports and forecasts, risk assessment and compliance, and fraud detection can all be streamlined with the help of GenAI. Tasks such as invoice generation and processing, payments and billing have all been automated to some extent but can be further enhanced with AI.
Property operations: AI is already being implemented to better manage property operations, such as energy management. GenAI has the potential to take this even further with much more dynamic energy optimization. Security and access control can be further enhanced. Tenant chatbots will become pervasive, making processes such as maintenance requests, account information and rent collection even more efficient. Reporting can be more robust. Marketing and leasing processes can be significantly enhanced. Generation of marketing materials, tenant acquisition, leasing, and creation of presentations and reports will be impacted by GenAI tools.
AI implementation
Given the wide range of possibilities, real estate companies should start with developing a GenAI strategy that includes:
Use case selection and process transformation. This should include company-specific immediate, medium- and long-term applications. The approach of leveraging GenAI is about rethinking how existing activities should be performed. It’s a different mindset—a transformative mindset. A business case should be made as to how GenAI can help the business, and what those benefits should be.
Technology roadmap and selection. Conduct “buy/build/acquire/wait analysis” to develop a model and acquisition plan for GenAI implementation. Evaluate the infrastructure that will be needed and create a report with estimated costs and timelines.
Risk, governance and compliance. It’s important for leadership to work with their risk, compliance and legal teams, as well as those that have experience developing digital policies and procedures, to create guidelines to inform their GenAI strategies. Develop a scalable AI governance framework and continuation monitoring processes. Engage in dialogue and conduct scenario planning to mitigate risk and create a plan that puts the organization in the best position to succeed.
Organizational transformation roadmap. Build a plan for what GenAI should look like as it is being implemented and then at regular intervals going forward. Formalize both an internal adoption strategy and an organizational transformation roadmap so that goals can be outlined and accountability maintained.
Talent strategy. Adoption of GenAI will require current talent to upskill themselves on new technology and may require hiring new talent. It will also have an impact on future resource count, especially in areas where GenAI has the most potential to introduce transformation. Aligning people strategy with business strategy is important to drive enterprise transformation.
There is now a proliferation of tools available in the marketplace to start implementing GenAI capabilities. In addition to a cloud infrastructure, key foundational elements of a technology stack required for GenAI include:
Foundation models. These models are trained on a broad set of unlabeled data that can be used for different tasks. Real estate companies will need to build capabilities on top of a foundation model.
Data storage and retrieval. In order to build GenAI applications, real estate companies will need to build capabilities, such as a semantic layer, to efficiently store and retrieve both structured and unstructured contextual data. Most of the real estate use cases mentioned above rely on access to internal as well as external data.
Models and applications. Fine-tuned models and applications will need to be developed for specific use cases. There are application frameworks available that can help to accelerate the development and deployment of models. GenAI tools that help to enable some of the use cases described above have already begun to be developed and will improve over time.
Hosting options. There are two options to host foundational models: third-party hosting or self-hosting (e.g., Azure). Which option is used will determine the encryption and security levels for the models, prompts and data. A self-hosting option can be more secured, allowing for automatic encryption and private end points. This critical decision is required to gain the trust of customers and end users and to comply with relevant regulations.
Umar Riaz is EY Americas Real Estate, Hospitality & Construction Consulting Leader.







You must be logged in to post a comment.